EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.
How EY can help
-
Addressing an organization’s overarching end-to-end supply chain and operations strategy to grow, optimize and protect their operations.
Read more
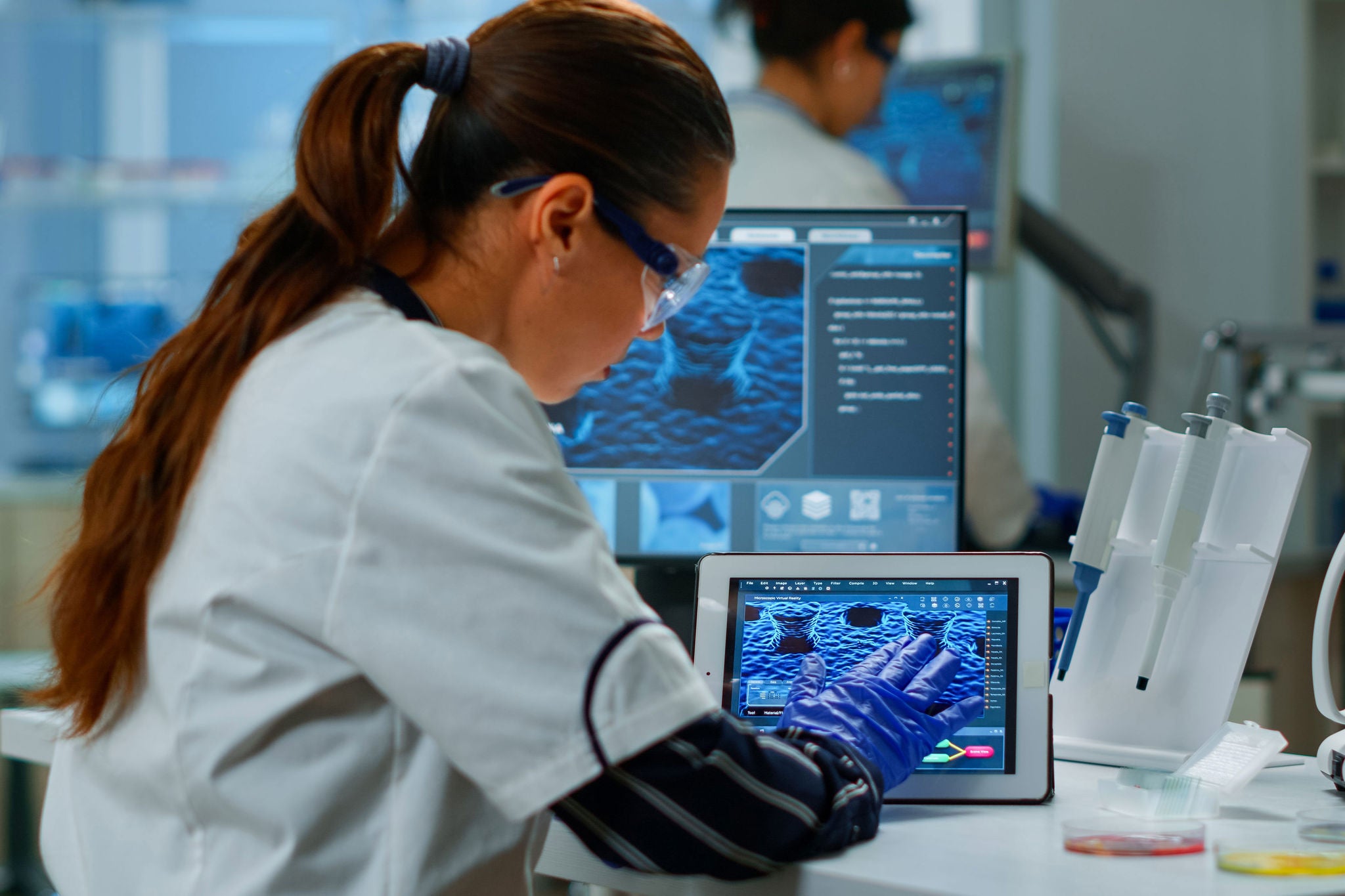
The RBE management process creates a direct focus on the deviations that have occurred during the process, providing the right personnel with the most critical information. The review also has a predefined designated order of signatures to respect any approval workflows that must exist to release the batch record. Once RBE has reached a mature state, some key benefits will be realized:
- Right-the-first-time records: RBE creates an emphasis on exception trends, providing the information of where to apply corrective actions in the process to eliminate deviations from occurring.
- Reduction of cognitive load: By eliminating manual calculation and information transcription, quality assurance can significantly reduce batch record review time.
- Paper elimination: Converting to an electronic system creates value by eliminating paper on the production floor during execution and in the file storage archives.
3. Success factors
The value of MES and RBE is tremendous; however, it is not simply achieved overnight. Going through the evolution of a paper master batch record (MBR) to an EBR can take several iterations of prototyping demonstrations and dry runs. This thorough design and review process enables end users to have a desirable batch record that can be executed without confusion or disruption. The execution of a well-designed EBR is only as successful as the training provided to the end user prior to go-live. Providing adequate and timely training to this audience is highly critical. Higher comfortability with the electronic system will also reduce the likelihood for unnecessary process exceptions to occur, minimizing extra work for quality assurance on the reviewing side. Involving the key end users of an MES system — manufacturing and quality — as early and as often as possible can largely attribute to a successful EBR and RBE deployment.
Lastly, a key consideration to fully taking advantage of RBE functionality will involve trust and taking leaps of faith with the new technology. The more elements of design, such as automatic calculation or electronic signature, that can be incorporated into the EBR design will result in more value generated in the RBE process. Early on, this journey might require some walking before running. The change management process is critical for end users to fully absorb the value of an RBE process in MES.
4. Next evolution
The transformation of batch record review from a full-manual process to RBE with an automated triggered review process has been a breakthrough. Allowing reviewers to see only process deviations provides them the ability to identify where continuous improvement opportunities can be implemented. Through RBE, it should be expected to see more analytics to identify reoccurring process deviations where corrective actions should be applied and the “right-the-first-time approach” can be achieved. With this framework in mind, human involvement in RBE should be reduced, but it will still be a key component.