Rethinking learning and building an adaptive workforce
Creating an adaptable workforce involves not only defining the technical skills needed, but also developing capabilities that support collaboration, agility and innovation - capabilities that will support teams in adapting and learning new skills.
The ability to react, pivot and evolve are critical foundational capabilities that support learning and upskilling. It’s not as simple as defining the skills and capabilities, as the statistics show that learning in its traditional form is not meeting the needs of many organizations, despite significant spend.² To drive meaningful, transformative outcomes and build a future-ready workforce, traditional learning methodologies and approaches must be reimagined to support the development of an employee base that can pivot with disruptions as they come up. This includes creating a culture that supports, prioritizes and rewards learning and embraces innovation in learning methodologies.
Integrating learning and work
Learning has historically been focused on specific training tasks, for example, reskilling farmers to operate new machinery. With today’s speed of disruption, by the time training has been developed and deployed, both the “machinery” and the skills are outdated. Behavioral science has shown that only 10% of human learning is happening through traditional learning, in mediums like online courses and instructor-led classes. While a small percentage, this 10% is important, foundational knowledge upon which other learning can be built. Organizations need to ensure they get the right content for 10% and then prioritize development efforts where 90% of effective learning happens – on the job.
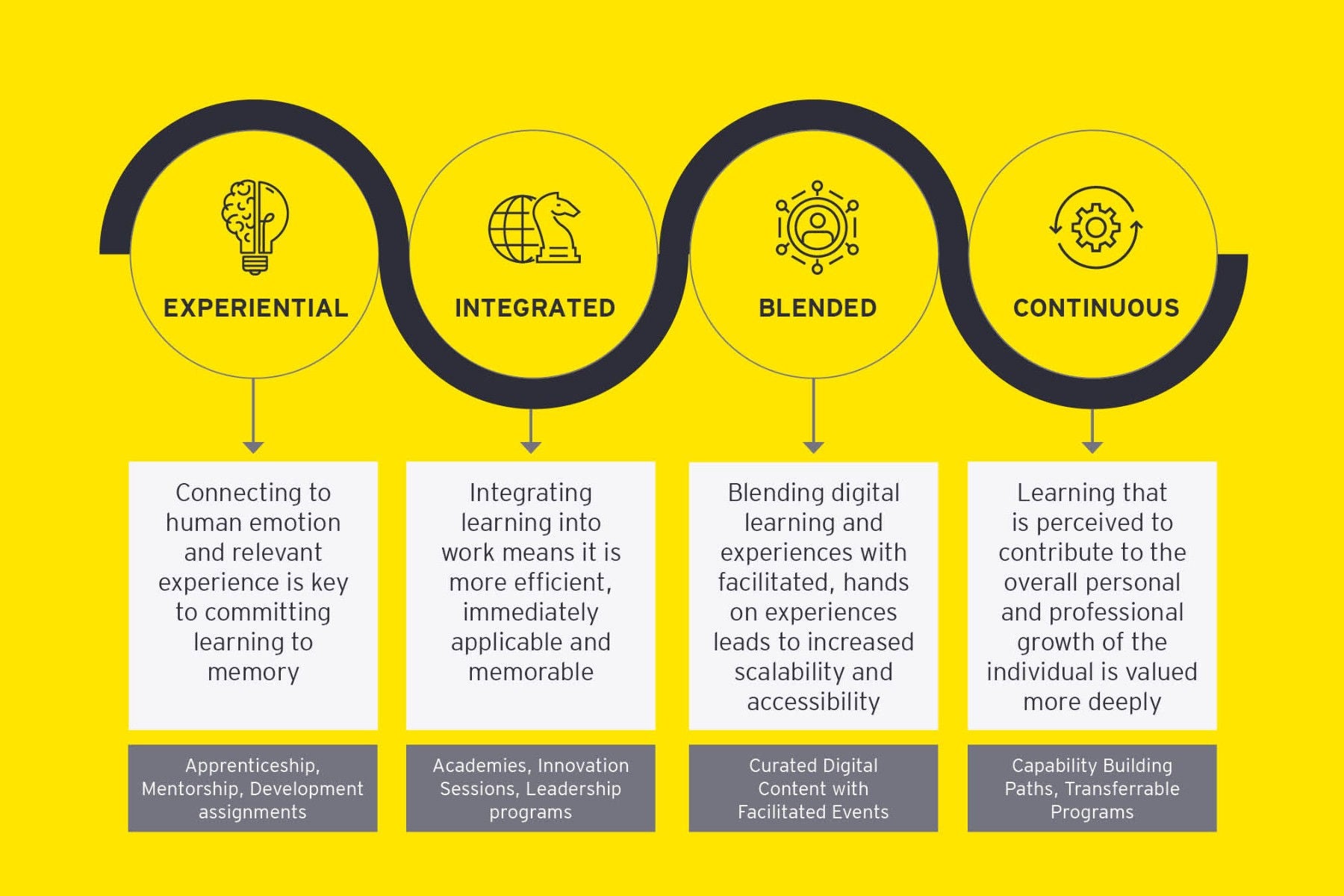
At EY, we define “embedded learning” as a process that makes learning explicit and integrates learning with work, rather than treating it as a series of separate events, like virtual classroom sessions. Learning embedded in everyday work can include on-the-job-coaching, apprenticeships, shadowing opportunities or business problem-solving in a supported environment – or a combination of these methods. Embedded learning is a key enabler in continuous business improvement. As ways of working evolve and organizations support more innovation and collaboration, embedded learning enables quick responses to mistakes and continuous development opportunities, ultimately improving results. Embedded learning has an additional benefit compared to traditional learning — since learning doesn’t take place all at once, your teams aren’t off work for extended periods of time. This provides a more cost-effective approach over time.
What differentiates “embedded learning” is that learning becomes experiential, work integrated, blended and continuous. Employees are likely to see the connection between their jobs and training when they apply their learning opportunities alongside daily work routines. Corporate culture should support a sustainable learning environment, integrating learning and promoting knowledge-sharing and collaboration among employees. One challenge today with integrating learning and work is the tracking and measurement of skill growth. While it is a challenge today, integration of data from learning management systems (LMSs) and learning experience platforms (LXPs) with operational data can allow for greater visibility into learning outcomes. Furthermore, evaluation of skill gaps before and after learning, focused on the actual application of the skills learned, can provide a more fulsome measurement.