EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Limited is a Swiss company with registered seats in Switzerland providing services to clients in Switzerland.

As crypto assets transform finance, we explore how to navigate and manage risks with the C-RAM framework, smart contracts and analysis tools.
In brief
- Crypto assets have revolutionized finance, reshaping economic transactions globally.
- However, this rapid expansion comes with risks that demand precise assessment and mitigation.
- Assessing risks with C-RAM, leveraging smart contracts, and embracing tech-driven analysis tools are key ways to practice solid crypto asset risk management.
In the dynamic world of finance, the introduction of crypto assets has fundamentally changed the landscape of economic transactions. Their decentralized nature and quick market adaptability have not only expanded the scope of financial intermediation but have completely reshaped interactions within the global economy.
Since 2010, the total market capitalization of crypto assets has grown from virtually zero to USD 1.31 trillion in October 2023, marking a drastic change in the financial landscape.
However, amid this rapid expansion is an urgent requirement to evaluate and mitigate the risks linked with digital assets. In this article, we dissect the risks of digital assets, introduce innovative solutions and explore how blockchain and smart contracts can fortify your financial ventures.

Chapter
The rise of crypto
How digital assets reshaped the financial landscape.
For the past few years, cryptocurrencies have been transforming the financial landscape like no other asset before. Back in 2009, Bitcoin debuted as the cryptocurrency breaking away from monetary systems. Its initial value was virtually negligible, but by 2021 Bitcoin’s market capitalization had skyrocketed to over a trillion dollars. The remarkable expansion that we are witnessing not only indicates the growing acceptance of digital currencies but also reflects the high standing among investors.
Bitcoin’s success has paved the way for other cryptocurrencies that bring unique functionalities and applications. A notable case is Ethereum, which came into existence in 2015 and was the first crypto currency to introduce smart contracts, agreements that automate complex transactions without any intermediaries. As of 2021, Ethereum’s market capitalization exceeded USD 400 billion, solidifying it as a key player in the world of cryptocurrencies.
And Bitcoin and Ethereum are not the only players on the scene. The crypto market has experienced rapid expansion, with thousands of tokens and coins entering the scene. Binance Coin (BNB), which is affiliated to the Binance exchange, has emerged as a key player in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. Its market capitalization exceeded $60 billion by 2021. Indeed, the surge in cryptocurrencies has attracted investors and institutional players alike. Companies like Tesla and Square have made investments in Bitcoin, with Tesla allocating a USD 1.5 billion to the cryptocurrency early in 2021. Moreover, traditional financial institutions have started incorporating cryptocurrencies into their offerings, while major banks are exploring the potential of technology and digital assets.
The impact of this crypto revolution extends beyond finance. It has sparked a discourse about the very nature of money, the central banks’ role, and the future of the global commerce. Governments are starting to question the regulatory implications arising from this shift and acknowledge the importance of establishing frameworks that balance innovation and risk with consumer protection.

Chapter
Understand the risks
Discover the C-RAM Framework, a tool that assesses and manages risks within the world of crypto assets.
As we mentioned earlier, digital assets come with a set of risks which need to be identified and evaluated. One effective approach is using the Crypto Risk Assessment Matrix (C-RAM) model. This advanced tool has been carefully designed to provide assessments of risks associated with cryptocurrencies. It operates through a three-step process that applies on both national and international levels.
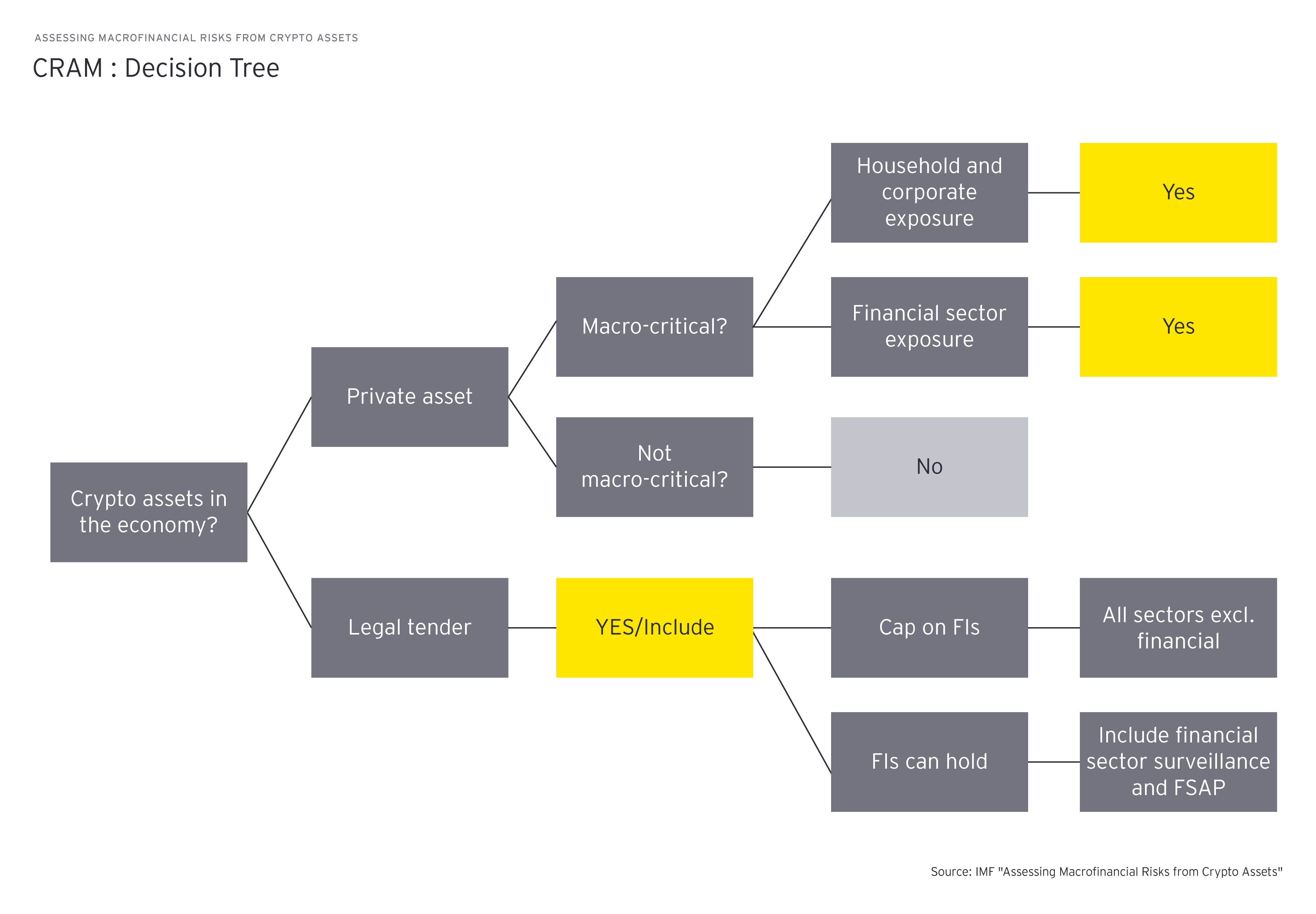
Firstly, the decision tree stage focuses on determining the macro criticality of crypto assets within an economy. It examines how crypto assets are being utilized within a given country. This assessment distinguishes between assets used as legal tender and those held as private assets.
For example, let’s imagine a situation where a country has adopted a specific cryptocurrency for daily transactions, even recognizing it as an official form of payment. This is the case for El Salvador and the Central African Republic, which declared bitcoin as official currency in 2021 and 2022, respectively. This indicates a high degree of macro criticality, meaning that the crypto asset plays a substantial role in these countries’ financial activities.
On other the hand, in a different country, individuals or businesses might use digitals assets for specific purposes but they may not hold the same level of significance on a larger scale. In this case these assets may not function as legal tender but rather serve as instruments for private or specialized transactions. Understanding this distinction is crucial when assessing how crypto assets are integrated into and impact the economy of a nation.
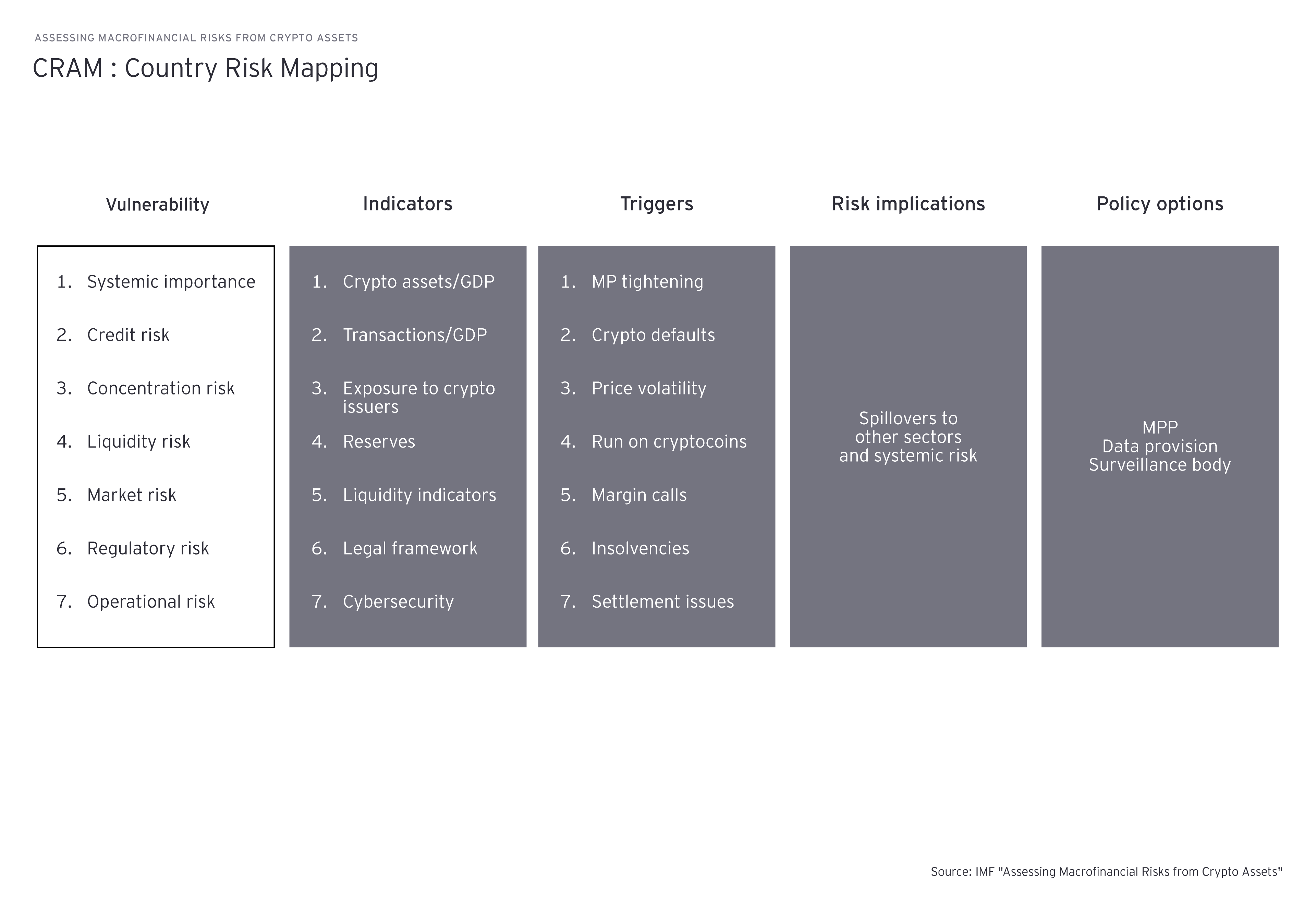
The second step is country risk mapping. This phase involves conducting a quantitative assessment of the risks associated with cryptocurrencies within a specific economy. A risk matrix enables thorough analysis of various aspects of risk across these seven distinct vulnerability groups:
The third and final step of C-RAM focuses on assessing the risks related to crypto assets on a global level. This step is crucial as it has implications for both the stability of economies and the broader global financial system.
Let’s imagine a scenario where a particular type of cryptocurrency gains widespread acceptance and is adopted by countries. This widespread adoption could potentially intensify market volatility and systemic risks, impacting not only economies but the global financial ecosystem.
For example, if a cryptocurrency becomes commonly used for border transactions it could influence exchange rates and potentially affect the stability of national currencies. Extensive adoption could potentially influence trade balances, capital flows and monetary policies across different countries.

Chapter
Risk management with smart contracts
Smart Contracts and EY's Blockchain Analyzer: A Dynamic Duo for Digital Asset Risk Management
Once risks related to assets have been assessed and identified, it is important to establish strong measures for risk mitigation. This is where smart contracts come into play. A game-changing solution, smart contracts revolutionize the way transactions are conducted by harnessing technology to automate and enforce agreements eliminating the need for intermediaries. These self-executing contracts provide a transparent framework that ensures transactions occur when predetermined conditions are met.
Smart contracts represent a milestone in the evolution of digital agreements. The concept was initially conceptualized by computer scientist Nick in the 1990s. It remained mostly theoretical until blockchain technology emerged. Platforms, like Ethereum, which came to life in 2015, provided a foundation for implementing contracts. These contracts contain predefined terms and conditions and trigger execution when specific requirements are met, without the need for intermediaries. This breakthrough has not only streamlined processes but also greatly reduces the potential for disputes and fraud across various industries.
Smart contracts also play a crucial role when it comes to risk management. For example, they can be designed to implement fail-safes and automated responses during times of crisis, which helps prevent broader system failures. To manage credit risk, smart contracts in lending platforms enforce requirements, ensuring that borrowers have collateral to cover their loans. If the value of the collateral falls below a threshold the contract can trigger a liquidation effectively minimizing credit risk.
Moreover, smart contracts can include measures to control the concentration of assets held by entities thus mitigating concentration risk. In terms of liquidity risk, decentralized exchanges and liquidity pools rely on contracts to maintain liquidity during volatile or low trading periods. These contracts adjust prices based on supply and demand to ensure a smooth trading flow.
Additionally, smart contracts can incorporate features like stop loss orders or price triggers to manage market risk. This means that if the price of an asset drops below a level the smart contract can execute a sell order to limit potential losses.
Using tools to analyze and interpret on-chain data can be a powerful enable of risk management
Finally, when it comes to regulatory risk, smart contracts can be designed to facilitate automated compliance with regulatory requirements. For instance, in a token sale, the contract can confirm the identities of participants and conduct verifications to ensure adherence to relevant laws. By utilizing these features smart contracts greatly improve risk management within the asset industry.
Smart contracts also generate a lot of on-chain data throughout the entire lifespan of a blockchain. Using tools to analyze and interpret this data can be a powerful enable of risk management in areas such as compliance and fraud prevention. It means organizations and financial institutions can benefit from the speed, accuracy and convenience of smart contracts while confidently navigating the changing landscape of digital assets with foresight and trust.
Summary
While crypto assets have completely transformed the financial landscape through decentralization, we must also acknowledge the potential risks that come with this shift. Our proposed C-RAM framework provides a way of assessing risks on both a global and country-specific level. An effective way to mitigate risks is by implementing smart contracts, which automate agreements and reduce counterparty risks. Using data-driven analysis tools can take risk management to a new level through insights into on-chain data.
Acknowledgements
We kindly thank Vadym Sheiko and Alexandre Caye for their valuable contribution to this article.
Related article
Leading the AI revolution: tangible opportunities in risk management
We provide research-based insights on the applications of artificial intelligence in financial risk management.




