EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.

New-age GCCs are increasingly adopting certain leading attributes to deliver strategic value to organizations.
In brief
- New-age GCCs are expanding their footprint to deliver decision-based activities and focus on innovation. They are now moving toward becoming a strategic partner for the enterprise.
- GCCs have gone beyond delivering traditional transactional activities and increasingly focusing on digitization, global systems integration, centralizing transformation office, etc.
Continuous innovation seen with Global Capability Centers (GCCs)
Last 30+ years have seen Global Capability Centers (GCCs) evolve, from single-function Shared Services to multi-functional digital-led Global Business Services (GBS) organizations. New-age GCCs are now delivering complex judgment and decision-based activities while continuing to centralize and automate the more transactional activities. They are leveraging technology to drive transformation and deploy a more agile operating model. More than just a cost-saving initiative, they are now seen as a truly strategic partner for the enterprise, and a source for sustained competitive advantage.
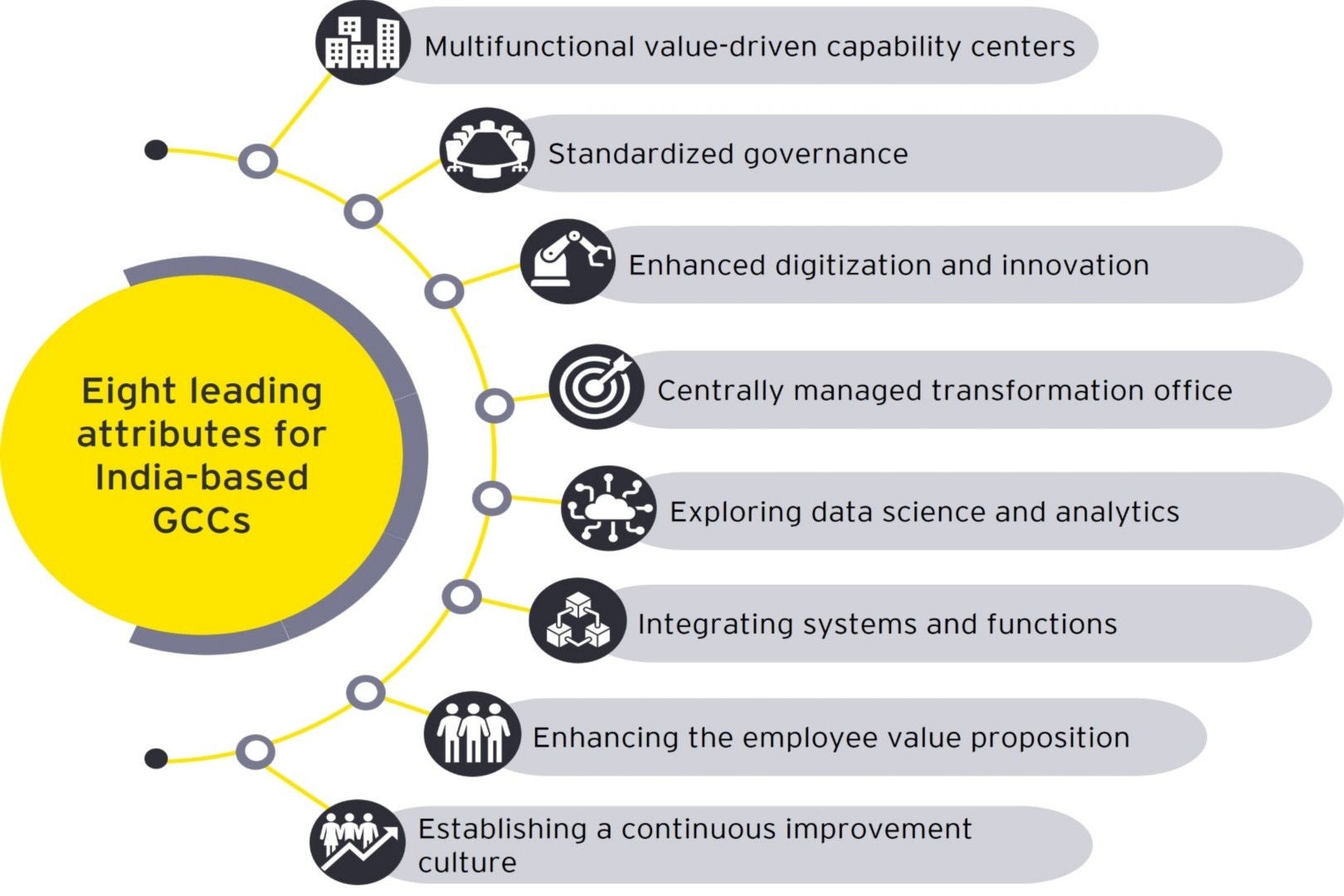
EY has identified eight leading attributes for India-based GCCs:
Our recent study identified the leading practices along with key initiatives, which mature GCCs are increasingly adopting to deliver strategic value for the organization. They are:
- Multifunctional value-driven capability centers: Leading GCCs have made single-function shared services delivering transactional services, a thing of the past. Today, the focus is on creating innovation in GCCs and delivering value across end-to-end processes. The focus now is on increasing the portfolio to include value-adding activities like data analytics, cloud services, financial planning & analysis, treasury, sustainability, logistics and warehousing, engineering R&D, etc.
- Standardized Governance: With unparallel growth in terms of scale, functions and complexity, there comes an increased need for a standardized approach to governance. GCCs have been quick to identify this, and have created standardized governance models spanning end-to-end processes, which are constantly updated. GCCs are adopting regular external benchmarking of Key Performance Indicators and Service Level Agreements (KPIs and SLAs), so as to maintain leading service levels. Multi-layer governance structures are being adopted as to deliver service excellence and operational transformation.
- Enhanced digitization and innovation: With access to leading talent in India, GCCs have taken up a larger role in driving digitization and innovation across the enterprise. By leveraging idea-sharing portals, organizations have been able to get some of the best ideas from their own employees, while also driving employee engagement toward innovation in the GCC. With emphasis on digital enablement in alignment with the broader organization goals, current processes are being made truly touchless and customer-focused. GCCs are taking a lead role in identifying and driving the innovation by introducing and testing new technologies (data lake, people analytics, robotic process automation, business intelligence reporting, etc.) at the GCC, which are then scaled across the enterprise.
- Centrally managed transformation office: Perhaps one of the major developments at GCCs has been toward establishing and expanding the transformation office. Organizations have actively worked on developing a structured and well-defined approach for the transformation office cutting across functions. They are working together with corporate and regional offices to identify process improvement opportunities and drive transformation initiatives across functions. The transformation office is also providing their resources for program managing initiatives within functions, which may not even be part of the GCC.
- Exploring data science and analytics: Organizations across the globe are shifting toward a more data and analytics based decision making process. In pursuit of this endeavor, GCCs have been constantly innovating on better applicability of functional tools, developing vendor portals, intelligent chatbots, analytical tools and emerging technologies, which can support the business across functions. Analytics Center of Excellence (CoE) is being set up within the GCC to deliver analytics services for all the business functions. Other initiatives include startup incubation hubs, intelligent automation CoEs, innovation hubs, etc.
- Integrating systems and functions: With organizations having operations in multiple geographies and businesses, there is an opportunity to better integrate systems across and within functions, for a smoother flow of data, and move toward a common source of truth. GCCs have been leveraging ERP systems for integration across the enterprise, while optimizing the number of ERP instances. Organizations, which have not yet moved to a common ERP instance, are also setting up Data Lakes to gather insights from multiple sources of transactional data and provide real-time dashboards.
- Enhancing the employee value proposition: One of the major challenges in the post-pandemic world, which every GCC is grappling with, is the talent shortage. As the talent market, especially for niche skills like digital, AI, ML, etc., continues to be highly competitive, GCCs have started focusing on developing compelling Employee Value Propositions (EVPs) to create a talent pull. With active focus on identifying skill requirements, they have tried to develop them, either through robust Learning and Development programs (L&D), giving cross functional experience to employees and partnering with leading business schools and engineering colleges for short-term programs. There has been a greater focus, than before, on effective capacity management to better utilize the available talent.
- Establishing a continuous improvement culture: With GCCs increasingly being given a larger role and responsibilities, the existing GCCs are on a continuous endeavor to optimize the current state operations. They have developed a culture of personal leadership and development with a focus on great customer service. Today, GCCs are deploying a dedicated Continuous Improvement (CI) team which works on processes improvement by utilizing the latest CI tools available in the market like Celonis, SAP Enable Now, Kanban boards, Document360, Pega, etc.
Summary
GCCs are continuously focusing on enhancing innovation and bringing in overall transformation. By increasing the scope of delivering digital services, value-adding activities, and leading transformation initiatives, GCCs are adopting modern leading-edge technologies and building niche skills at scale.
Related content
How can GCCs drive the ESG agenda in your organization?
Transform your sustainability function by creating a central team that seamlessly works with other functions to deliver the best ESG outcomes.
Chapter III: Zero Trust— the vigilant enterprise
The Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) in cybersecurity emphasizes a "trust but verify" approach, ensuring limited access and continuous evaluation for security.
How is data driving a new order for global capability centers (GCCs)?
Discover how GCCs are setting up centres of excellence that house experienced data scientists and engineers that are analysing volumes of data.
How EY can help
-
Our Global Capability Centers(GCC) Advisory practice, led by a team of professionals can help your business be future-ready for the digital disruption.
Read more -
EY partners with insurers to build digital-first transformation strategies, deploying tools that boost efficiency, performance, and customer experience
Read more -
Drive business growth with technology transformation solutions at EY - integrating tech, operations & architecture to build agile, data-driven organizations
Read more





