EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.

GenAI risks
Risks associated with GenAI, especially in LLMs, include model-induced hallucinations, ownership, and technological vulnerabilities such as data breaches, as well as compliance challenges arising from biased and toxic responses. There have been recent examples of authors being credited with non-existent articles and fake legal cases have been cited by GenAI tools. Inadequate control over LLMs trained on confidential data can lead to data breaches, which, according to a recent EY survey, is the single biggest hurdle to GenAI adoption in India.
Toxic information and data poisoning, intensified by insufficient data quality controls and inadequate cyber and privacy safeguards, adds another layer of complexity, diminishing the reliability of GenAI outputs and jeopardizing informed decision-making. Additionally, the broader spectrum of technology risks of deepfakes to facilitate crime, fabricate evidence and erode trust necessitates proactive measures for secure GenAI adoption.
Potential intellectual property rights (IPR) violations during content and product creation also raise legal and ethical questions about the origin and ownership of generated work.
Other risks include:
- Bias and discrimination
- Misuse of personal data
- Explainability
- Misuse of personal data
- Predictability
- Employee experimentation
- Unreliable outputs
- Limitations of knowledge
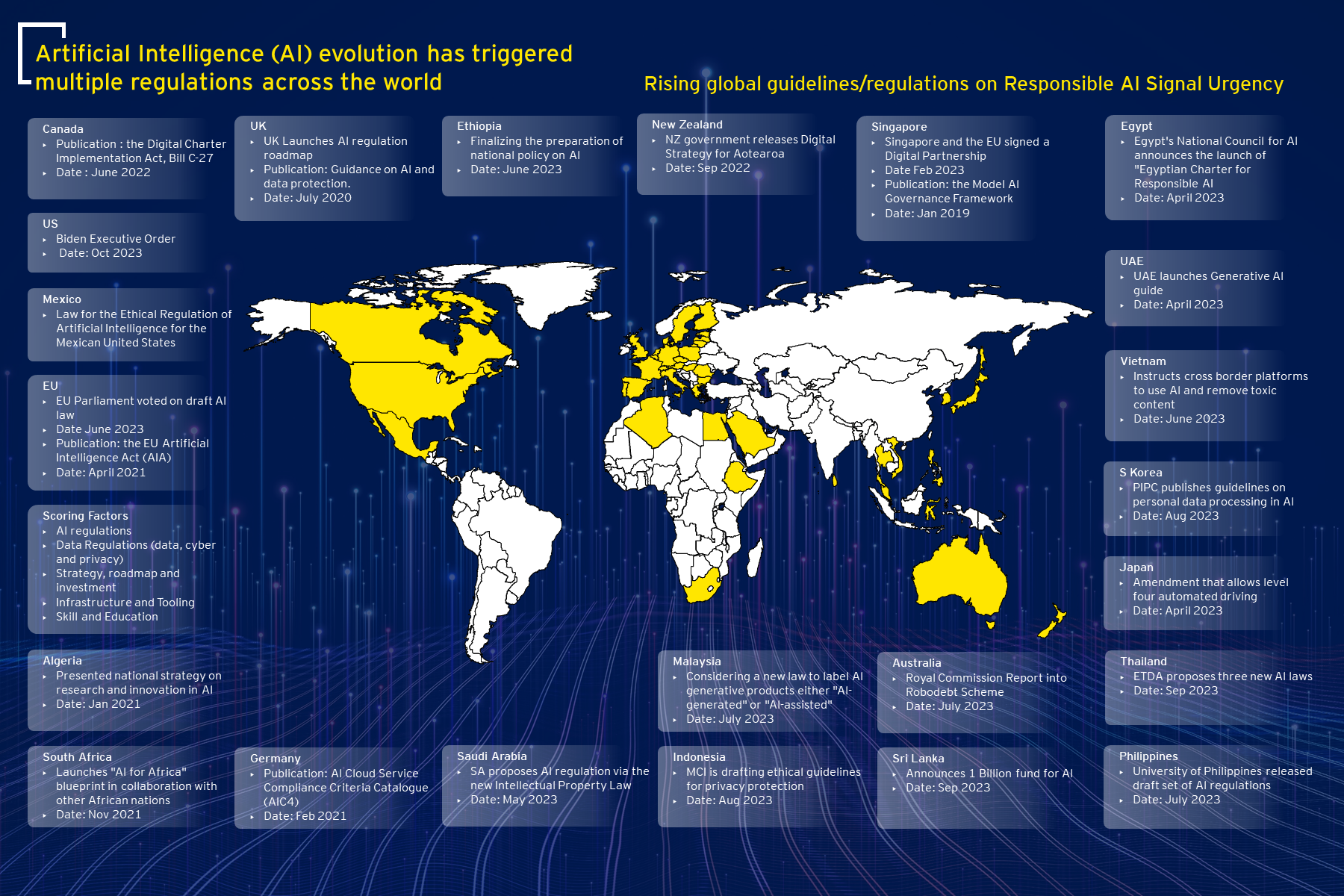
- Evolving regulation
- Legal risks
Building guardrails against risks
To capitalize on the competitive advantage and drive business, GenAI models and solutions are implementing safety guardrails to build more trust. The tech giants have created the frontier model forum. Its objectives include advancing AI safety research, identifying best practices, and collaborating with policymakers, academics, civil society, and companies. The forum aims to ensure that AI developments are handled responsibly and deployed responsibly. A model’s performance is evaluated and measured against designated test sets and quality considerations. Model monitoring and performance insights are leveraged to maintain high quality standards.
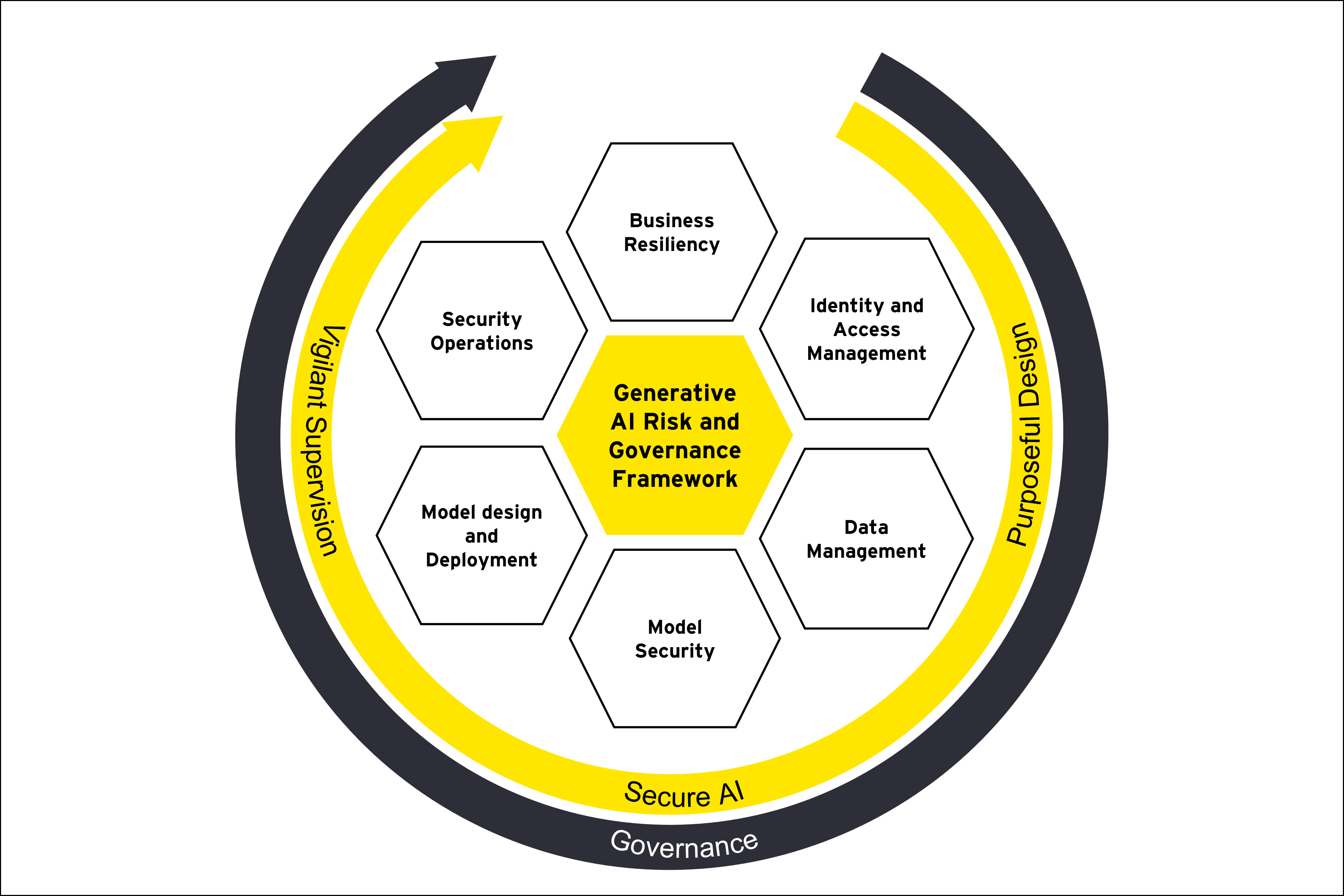
With various models evolving, implementing robust data governance policies that comply with privacy regulations will help companies mitigate risks. There are seven key domains to establish a robust framework and governance processes that align with industry-leading standards of responsible AI. These are business resiliency, security operations, model design development, governance, identity and access management, data management, and model security.