EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.
One of India’s leading FMCG organizations, HUL, is driven by the purpose of creating a common practice of sustainable living.
ESG is an enterprise-wide agenda for many, but when an FMCG major whose brands can be found in nine out of 10 households in India decides to make it a mission, one can expect big results. Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL) started its sustainability journey more than a decade back and has added many feathers its cap along the way. From embarking on its sustainability journey in 2010 with a public commitment to sustainability as part of the Unilever Sustainable Living Plan (USLP) to being recognized by the World Economic Forum in 2022 for sustainable practices, HUL has built core strengths in ESG.
The INR 50,000 crore-plus turnover company became plastic neutral in 2021 and has achieved zero waste to landfill. It has empowered more than 150,000+ women in rural areas and provided support to micro-entrepreneurs to create livelihood opportunities in their homes. For the FMCG major, sustainability equals business and business equals sustainability, which is reflected in its three core beliefs:
Companies with purpose last
Brands with purpose grow
People with purpose thrive
The Unilever Compass provides direction globally toward improving the planet’s health. It is improving people’s health, confidence, and wellbeing, is and contributing to a fairer, more socially inclusive world. Sustainable business transformation is essential for growth and HUL relies on strategy, innovation, and technology to make its ESG framework effective.
HUL’s next milestones include becoming net zero by 2039. By 2030, the company aims to halve the intensity of carbon emissions in their product range. HUL is addressing water shortage as a business, social and environmental priority. It is undertaking a program to create a water potential of 3 trillion liters.
As many organizations believe that sustainability is key to a thriving business, it is important to manage priorities and deliverables that are sustainable in the long run. For example, at HUL, the senior leadership is rewarded for long-term performance in sustainability and even day-to-day operations are evaluated based on the ESG criteria.
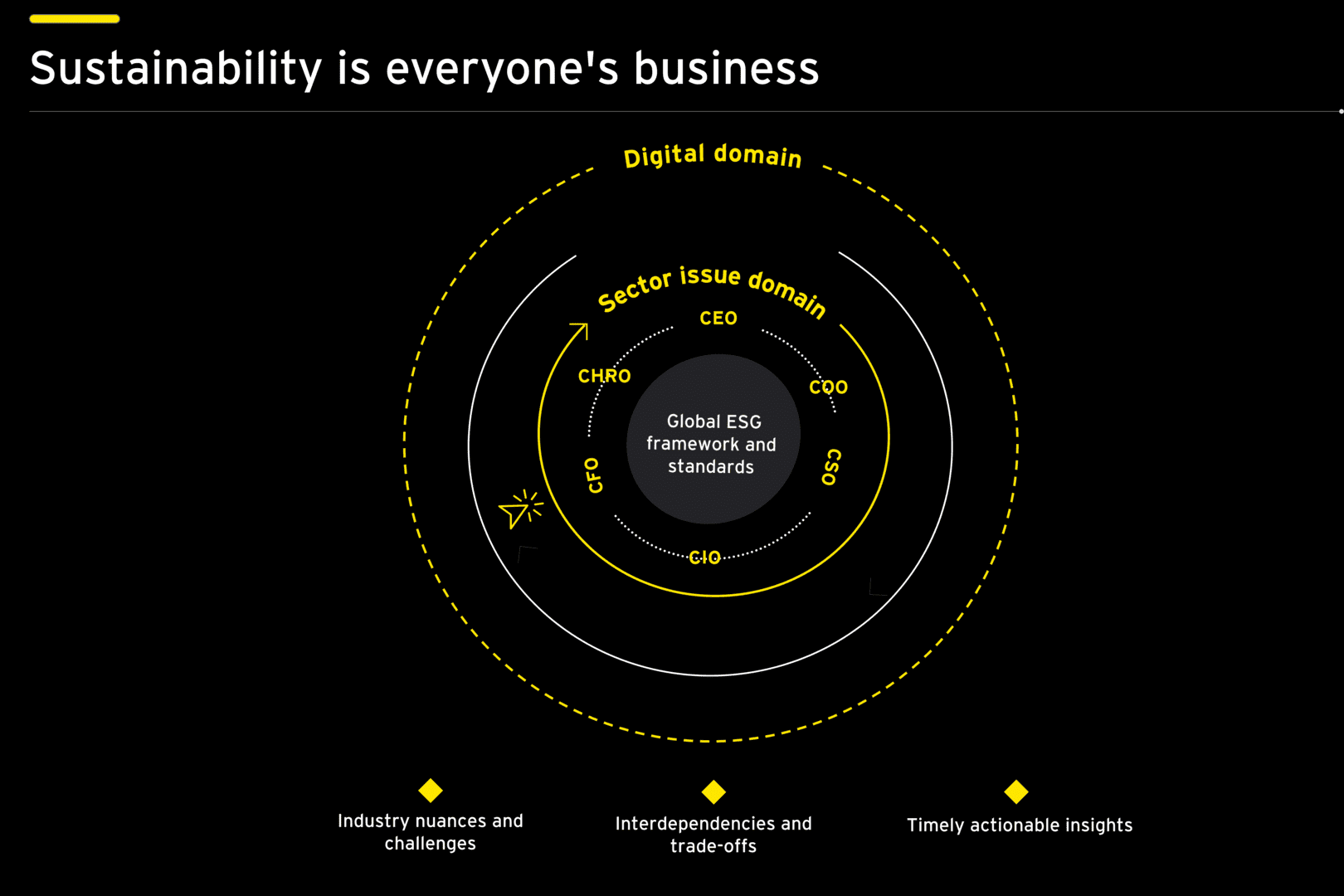
In the sustainability journey, technology will play a key role while resources will have to be sourced from multiple organizations. ESG is not a zero-sum game; every company will have to lean in and join forces.
EY has been collaborating and partnering with HUL for the last two years in this complex journey, including:
1. Sector benchmarking and FMCG leading practices
2. Capacity building across key functions
3. ESG Governance and process framework
4. Non-financial reporting framework
5. ESG data analysis and maturity
6. Communication framework and Rating IQ intelligence
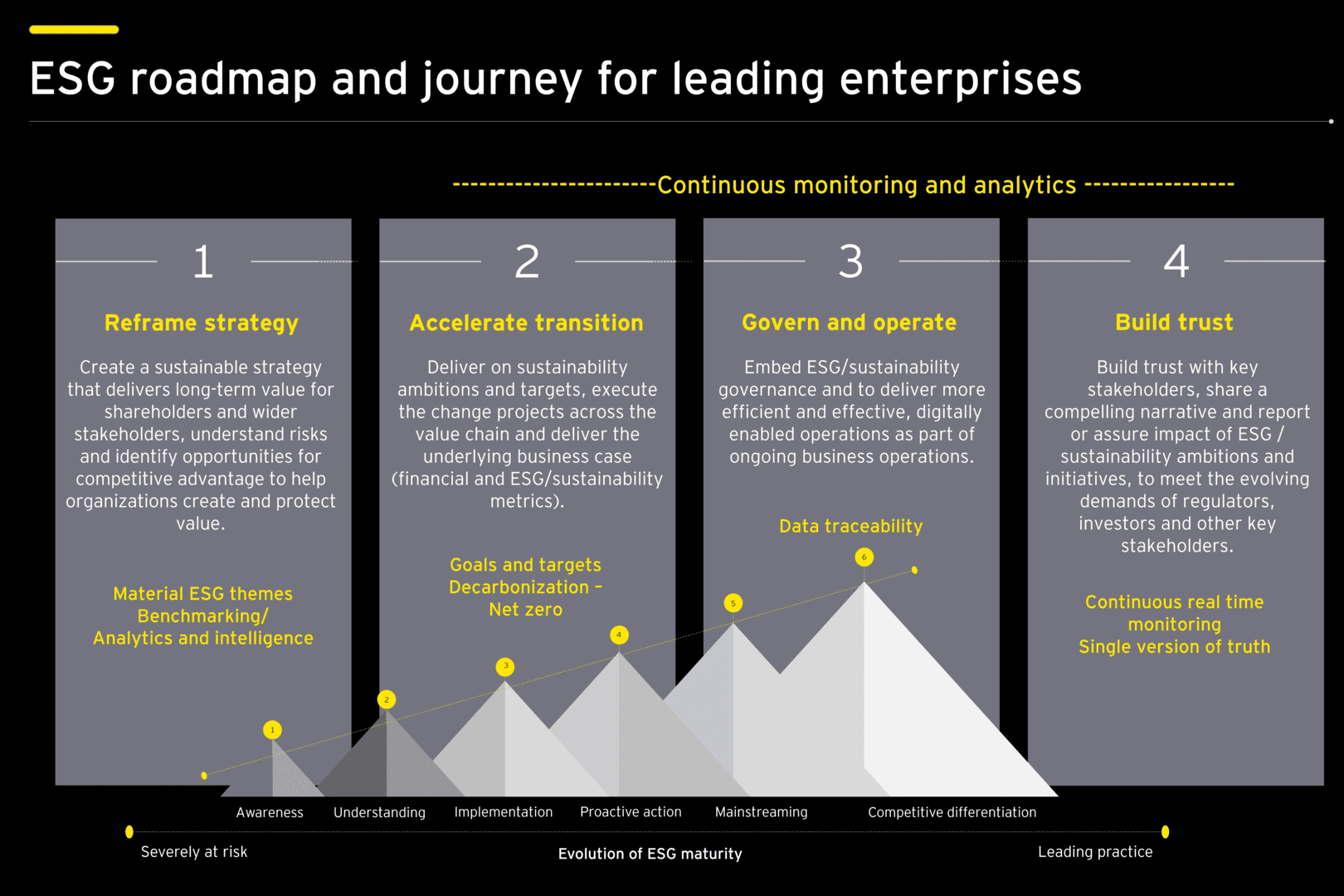
Measuring ESG
For leading enterprises, ESG is a focused board agenda to create and protect value. It is important to have consistent and comparable scientific measurement of sustainability variables across all stakeholders so that there is a single version of truth with real or near-time performance analytics to create actionable insights.
Accordingly, an ESG framework’s purpose must be based on four pillars:
- Scientific measurement and base lining
- Benchmarking and continuous analytics and early warning signals
- Improving performance to enhance revenues, optimize cost and working capital
- Effectively communicate the impact and outcome across all stakeholders
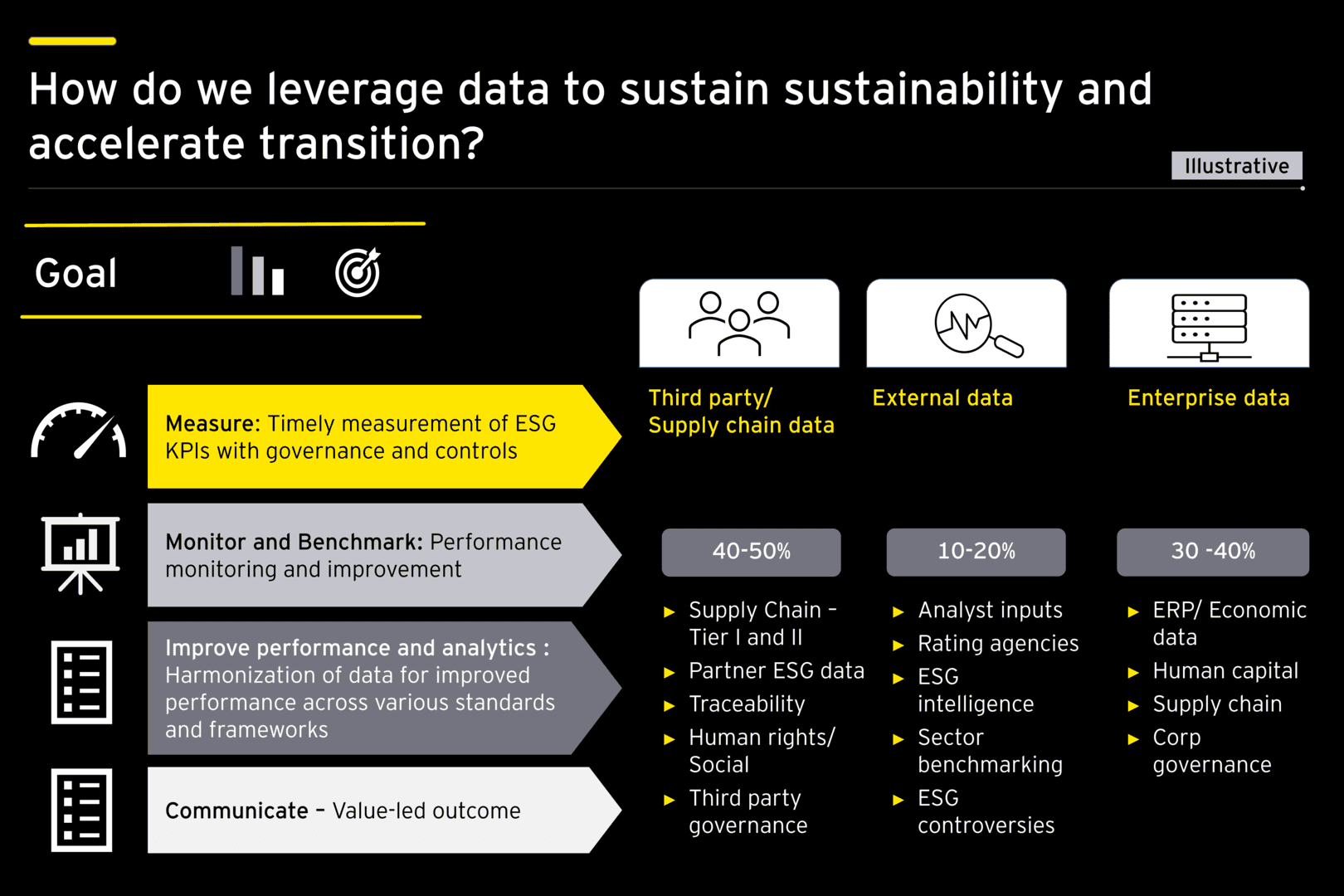
To make crucial business decisions, data needs to function as both a telescope and a microscope. Additionally, there are three primary data models from an ESG perspective:
- Enterprise data that an organization emits across its business model: The main focus would be on the core business functions of buy, make, move, and sell, which are supplemented by processes like H2R (hire to retire), R2R (record to report), and governance processes.
- Third-party data across supply chain: Having third-party data across Environmental, Social and Governance metrics for key suppliers, business partners, distributors, outsourced service providers and customers – is key for traceability from cradle to cradle.
- External data that the outside environment is creating: Various sources such as consumer sentiment analysis, investor/analyst inputs, ESG controversies, competitor intelligence, sector benchmarking, and corporate social data are generating information that can be used for intelligence
Third-party and external intelligence is key to differentiating an enterprise’s ESG transformation journey.
Not just organizations, consumer and employee perspectives have also changed over time and various other stakeholders, including investors and governments, want higher accountability from organizations.
Our recent analysis of EY’s Future Consumer Index Survey indicates that there is a growing demand among customers for sustainable products and services. As many as 43% global consumers said they want to buy more from such organizations and are willing to pay more for certain categories.
More importantly, 64% of consumers said they are willing to change their behavior to help the environment and society. At the same time, investors want consistent and comparable ESG performance. This has, in fact, become critical to assessing by leaders in this space.
To build internal and external accountability, organizations on a sustainability journey must keep in sight three points of reference.
- The first is the current position. The organization needs to benchmark itself against peers to understand the current maturity
- The second point of reference is destination, which will determine the goals and the ambitions
- The third is to design a plan that will enable the organization to reach its target with periodic milestones
Role of digitization
With ESG becoming a mega-trend, there has been a significant increase in performance measurement, monitoring, and benchmarking data. In India, the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR) framework is an important step toward reporting on non-financial measures.
HUL has set up digital capabilities to ensure robust non-financial reporting and drive performance cadence in the organization. This also becomes a determinant in resource allocation, which is of significance given the very long-term nature of the sustainability commitments.
It is critical to map and analyze the interdependencies and trade-offs within the sustainability journey across multiple capitals and stakeholders. This multi stakeholder and capital model will help us both balance and accelerate the transition in a just manner
Robust systems and processes ensure accurate and transparent reporting across all non-financial parameters. The purpose is to bring clarity so that the reporting is a true reflection of business performance seen from the perspective of business sustainability. This is where digitization can play a huge role.
Based on its long and deep experience, according to HUL, the key takeaways for organizations embarking on their ESG journey, are:
- Leading organizations need a transition plan toward net zero
- Sectoral inputs are important for a tailored approach to ESG for the business model
- Collaboration and cross-functional teams are critical for success
- Data and digitization are crucial for accelerating progress
- Sustainability learning is key to create knowledge of the emerging revolution
- Finance has a crucial role to play as stewards of ESG and building trust through data
Organizations that are on a long-term and large-scale sustainability transformation mission must build a roadmap that will not only provide direction but also help them address some challenges.
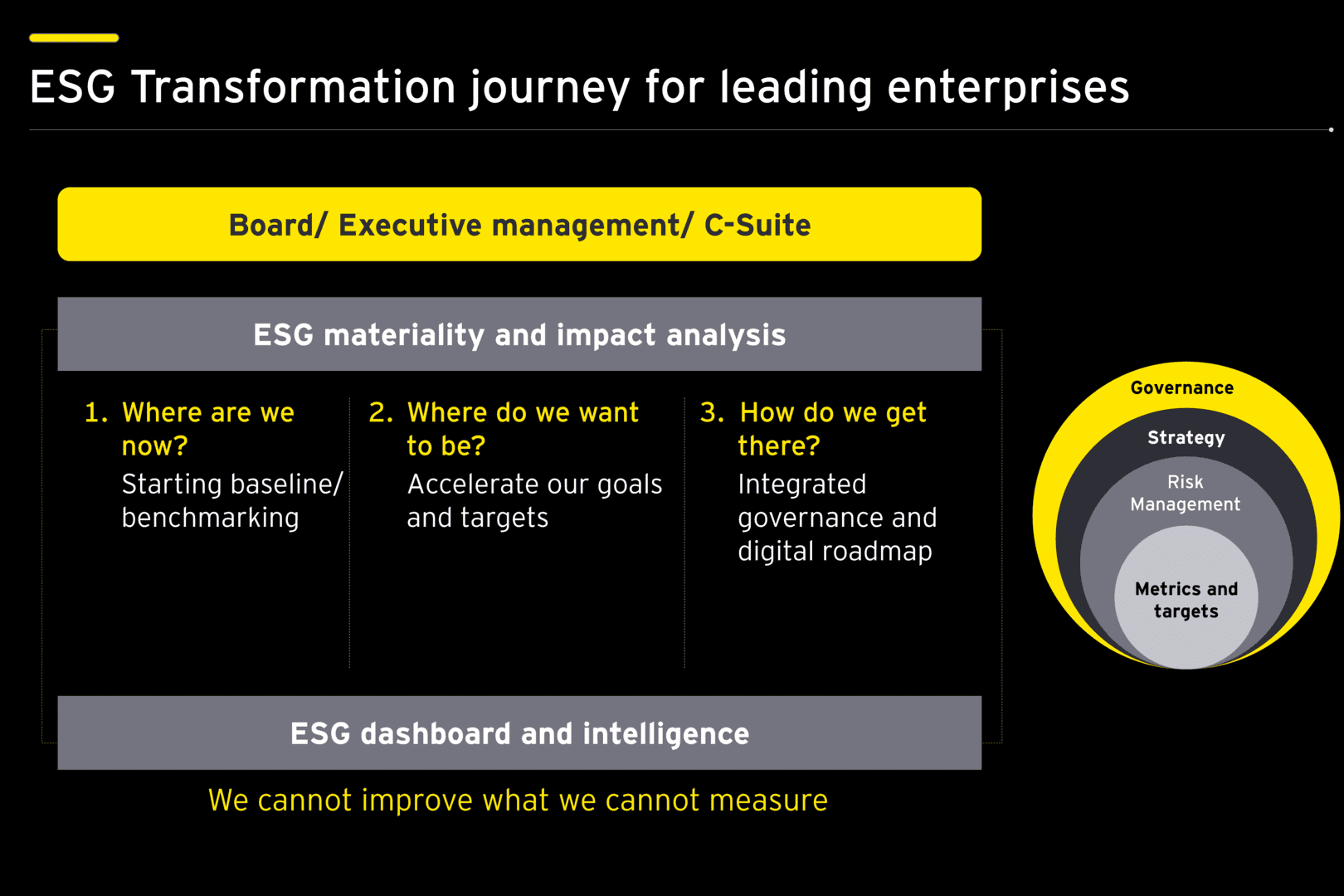
Critical success factors for sustainability transformation include:
We need technology@speed and innovation@scale with humans at the heart.
Summary
Sustainability is everyone’s business. India Inc. can contribute to a more sustainable future and create value for both their business and society by committing to sustainable practices. HUL's commitment to sustainability is an ongoing journey. It is striving ahead, driven by the belief that sustainable business drives superior business performance.
This is part of the Transformation Realized - Powered by EY series currently being hosted on CNBC, wherein we feature stories of business transformation led by India's most inspiring business leaders who have created value by placing human@center, deploying technology@speed and innovation@scale.
How EY can help
-
EY ESG & sustainability services help organizations address investor concerns, enhance ESG reporting and performance with long-term sustainable strategies.
Read more -
Streamline ESG reporting with EY’s ESG Compass. Explore ESG solutions, tools, dashboards, and fact sheets to enhance sustainability and compliance.
Read more
Related content
See how ICICI Lombard delivered value to all stakeholders through innovative, human-centered post-merger integration. Discover their strategic approach.
Watch how a global alcoholic beverages company adopted a cross-function digital strategy in India and saw accuracy in demand prediction improve by 25%.
Transformation Realized: Building a seamless healthcare delivery ecosystem
Watch the transformation journey of Sahyadri hospitals and Everstone enabled by EY. Learn more in this video from our Transformation Realized series






