Integration and hosting: key considerations
When it comes to software integration, the study reveals a preference for bundled solutions when they demonstrate ease of use and clear business benefits. However, the integration of different software solutions, particularly between computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) and simulation, verification and optimization (SVO) or product life cycle management (PLM)/CAD-to-CAM, is deemed essential for creating efficient workflows.
Cloud hosting and SaaS models are on the rise, with larger companies favoring these flexible options. Yet, the preference for on-premises solutions remains strong, especially among smaller manufacturers. The challenge for vendors is to offer adaptable deployment options that cater to customer preferences, leveraging modern cloud technologies for faster, more secure and efficient operations.
AI use cases in manufacturing
Looking ahead, AI emerges as a transformative force, particularly in feature recognition and CAD/CAM programming, streamlining processes and enhancing quality control. The integration of AI within manufacturing software is predicted to become more prevalent, heralding a new era of competitive advantage for those who adopt it early.
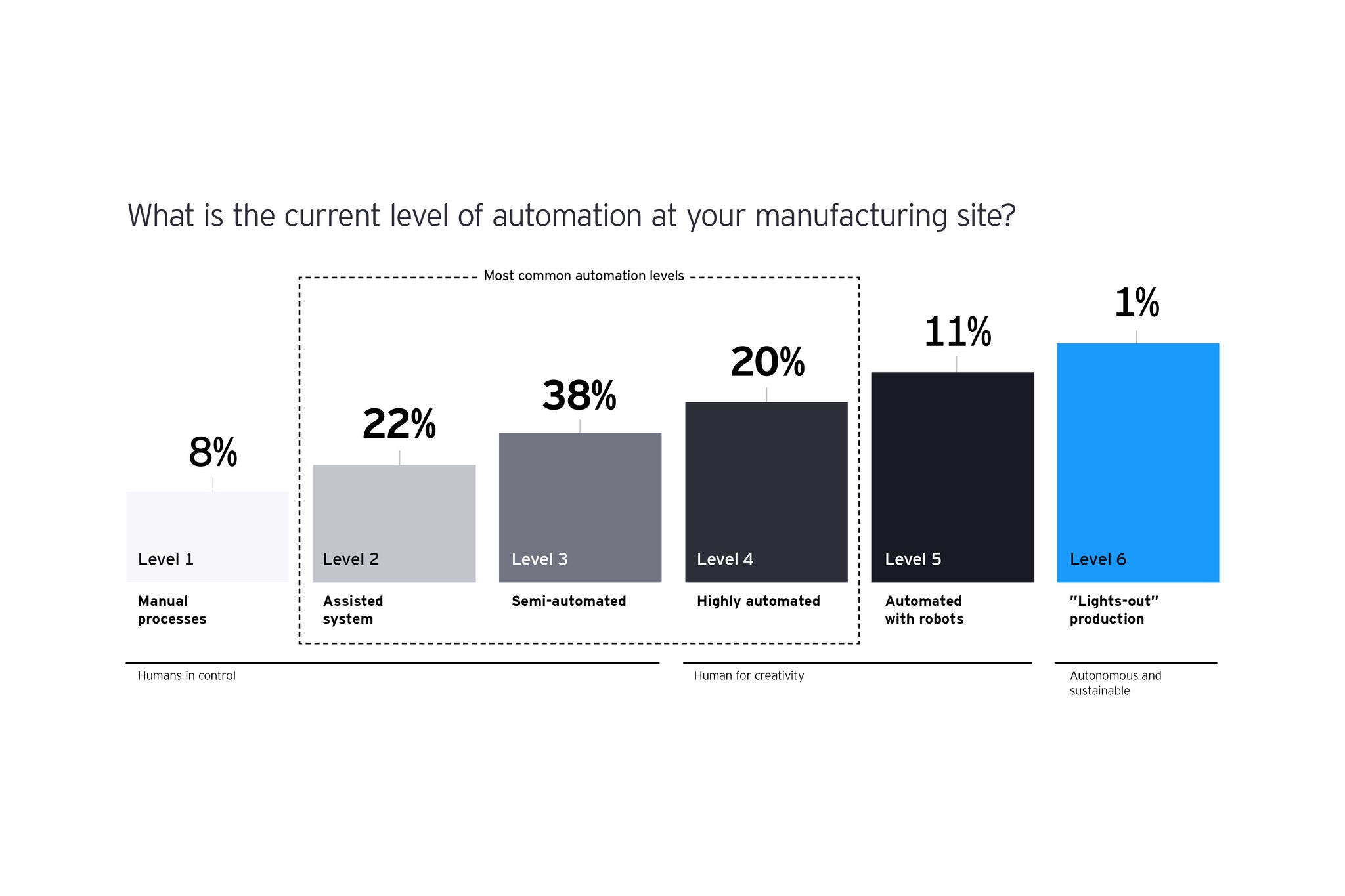
As human creativity continues to be a vital component, generative AI stands ready to redefine productivity and operational methods. It offers a vision of a manufacturing landscape enriched with intelligence, adaptability and innovation.
Ready to dive deeper into the software that's driving automation forward? Our full report offers a detailed examination of the current trends and future directions in manufacturing software.
Download the report — Trends in manufacturing software