EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.

The future belongs to firms who seize the potential of transformative technologies to shape the next generation of financial services.
In brief
- What are the biggest risk and opportunities in 2024 as technology and regulatory trends continue to reshape Southeast Asia’s financial services market?
- Where will generative AI (GenAI) generate the most value as institutions seek new levels of responsiveness in customer service, compliance and cybersecurity?
- How can incumbents get ahead of the curve to retain the customer relationship in cross-border transactions as well as embedded finance and insurance?
In 2024, Southeast Asia’s financial services (FS) sector will see the profound impact of emerging technologies and strategic innovation. In response to the region’s digital and social commerce growth, the sector will increasingly be characterized by instant cross-border payments, embedded finance and core banking modernization.
In the asset management sphere, the launch of the Variable Capital Company (VCC) 2.0 will allow Single Family Offices to use the VCC as an evergreen investment vehicle.
VCC 2.0 and the continued growth in wealth and family offices will position Singapore as the wealth capital of Asia.
But while the innovation opportunities are profound, inter-operability and cross-sector convergence will introduce new financial crime and payments risks.
Rapid increase in cross-border transactions
Southeast Asia is a flourishing market for cross-border e-commerce – a space where FinTechs are well-positioned to win share from banks. The region’s cross-border transactions increased rapidly in 2023, driven by economic growth, digital infrastructure development and growth in tourism.
Cross-border transactions have previously been hampered in places by the high cost, slow speed, lack of transparency and security concerns associated with remittances. But regulators, financial institutions and industry stakeholders have been collaborating around multiple initiatives to address these issues. 2024 looks to be the year where cross-border payment connectivity will be boosted across the Asia-Pacific by real-time payments, APIs and blockchain. Importantly for Southeast Asia, a local QR-code-based real-time payments ecosystem is taking shape.
In the year ahead, adopting ISO 20022 messaging standards will help to overcome interoperability challenges, providing consistent messaging globally for data flows across the FS sector. Institutions that don’t migrate in time could find themselves at a disadvantage – even excluded from payments networks.
Integrated fraud services and GenAI tackle financial crime
In 2024, one key area on the agenda will be the increase in fraud being driven by real-time payments, which afford little time for authentication. In response, institutions will increasingly make use of integrated fraud services, where transactions can be screened and (if necessary) blocked in close to real time. Multiple risk mitigation strategies are also likely become commonplace, with biometrics and behavior authentication used alongside passwords and multi factor authentication.
Meanwhile, Gen AI is expected to drive advances in identity fraud, with deep fakes increasing the likelihood of crime and rendering current KYC controls ineffective. In response, FS CISOs will need to add the same technology to the cybersecurity armoury. We expect investigation copilots will improve the consistency of decisions across volumes of data previously unmanageable for humans alone. Large language models (LLMs) will be used for transaction look-backs to significantly speed up transaction reviews by extracting relevant information, identifying transaction patterns and flagging suspicious activities.
We also expect to see FS firms training their own LLMs to increase responsiveness and agility. For example, an AI-enabled knowledge base trained on tailored banking data can support banking employees to quickly surface accurate information on current regulations, intricate product specifications or up-to-date security protocols. This will help to remove the burden of regulatory compliance, expedite customer service and fortify security measures. The result will be increased customer satisfaction, reduced risks and operational efficiencies.
Insurers must evaluate the impact of Gen AI on their business and make the most of the technology’s potential to improve, not just fraud prevention, but strategic planning, customer experience and claims management.
Exponential rise in embedded finance and insurance
2024 will also see non-FS companies increasingly embedding financial services in their core value propositions . This embedded finance (EmFi) will drive cross-sector convergence as finance components are invisibly integrated into customers’ purchasing experiences.
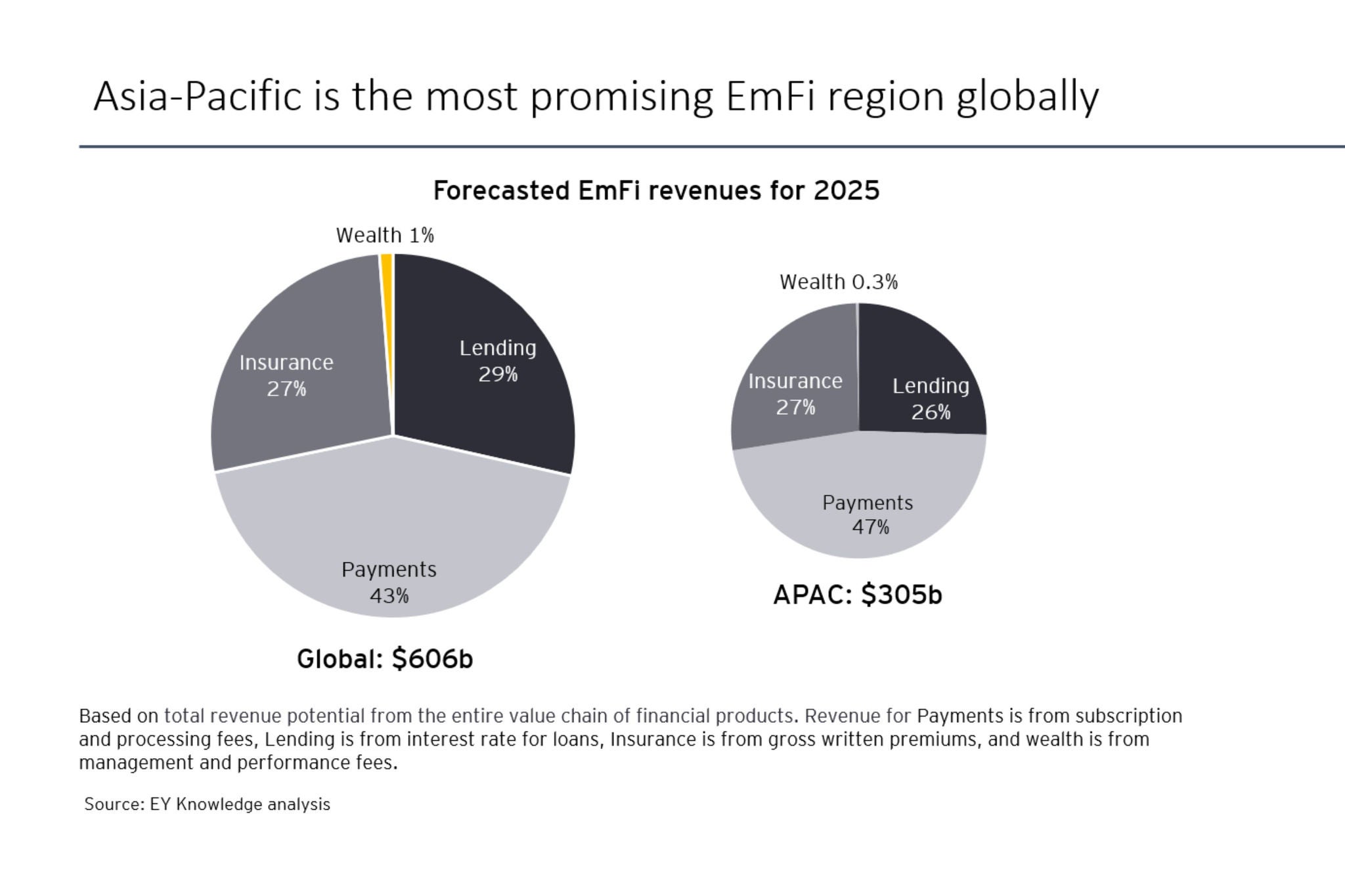
Embedded wealth could soon be disrupting the dynamics of wealth management. There’s real potential for retail banks, for example, to offer “brokerage-as-a-service” as a value add for customers with savings accounts. Equally, financial health platforms, which are already adding savings services, could similarly add on investment services.
Payment firms will capitalize on embedded payments by developing integrated payment solutions, leveraging data and AI, and providing value-added services. Insurance and lending will be the largest categories among the EmFi product spectrum, often bundled together.
EmFi presents FS incumbents with opportunities to explore new markets and reinvent their core businesses by partnering with third-party platforms to offer interoperable FS. The question is: How much of the EmFi market can traditional institutions secure?
With their core underwriting capabilities, insurers with bold embedded insurance strategies should be able to avoid disintermediation. Insurance-as-a-Service will be integrated with mobile apps and websites to purchase insurance with one click at the point of sale. Insurers are well placed to become a core element of this market alongside retailers and marketplaces, with platform partners connecting the two using pre-built solutions and accelerators.
Wealth and asset managers (WAM) may not be so well placed. The WAM sector has tended to lag others in the use of AI and technology. It will need to leapfrog forward by partnering with FinTechs to retain a place at the EmFi table.
In 2024, the most pervasive form of embedded lending is likely to be buy now, pay later (BNPL), with instalment products integrated into retail platforms. In Southeast Asia’s emerging markets, where a high percentage of customers struggle to secure traditional credit, BNPL providers can offer a financial lifeline. We therefore expect banks to use EmFi, in the form of BNPL, to promote financial inclusion.
Core banking modernization becomes easier
The 65% of FS IT budgets currently going toward “keeping the lights on” is untenable. Firms need to stop making modest adjustments to a decades-old, unwieldy assortment of systems, infrastructure and processes. The imperative is to evolve toward nimbler solutions that will reduce complexity and enhance operational efficiency, while enabling firms to innovate faster and provide the seamless, tailored experiences consumers demand.
In 2024, legacy simplification will be much easier thanks to the rise of open APIs that create a connected network of FIs, software suppliers and FinTech communities. By further combining APIs with organizational structures such as low and no-code platforms, modular technology architecture and microservices, institutions will be able to innovate faster and more cost efficiently.
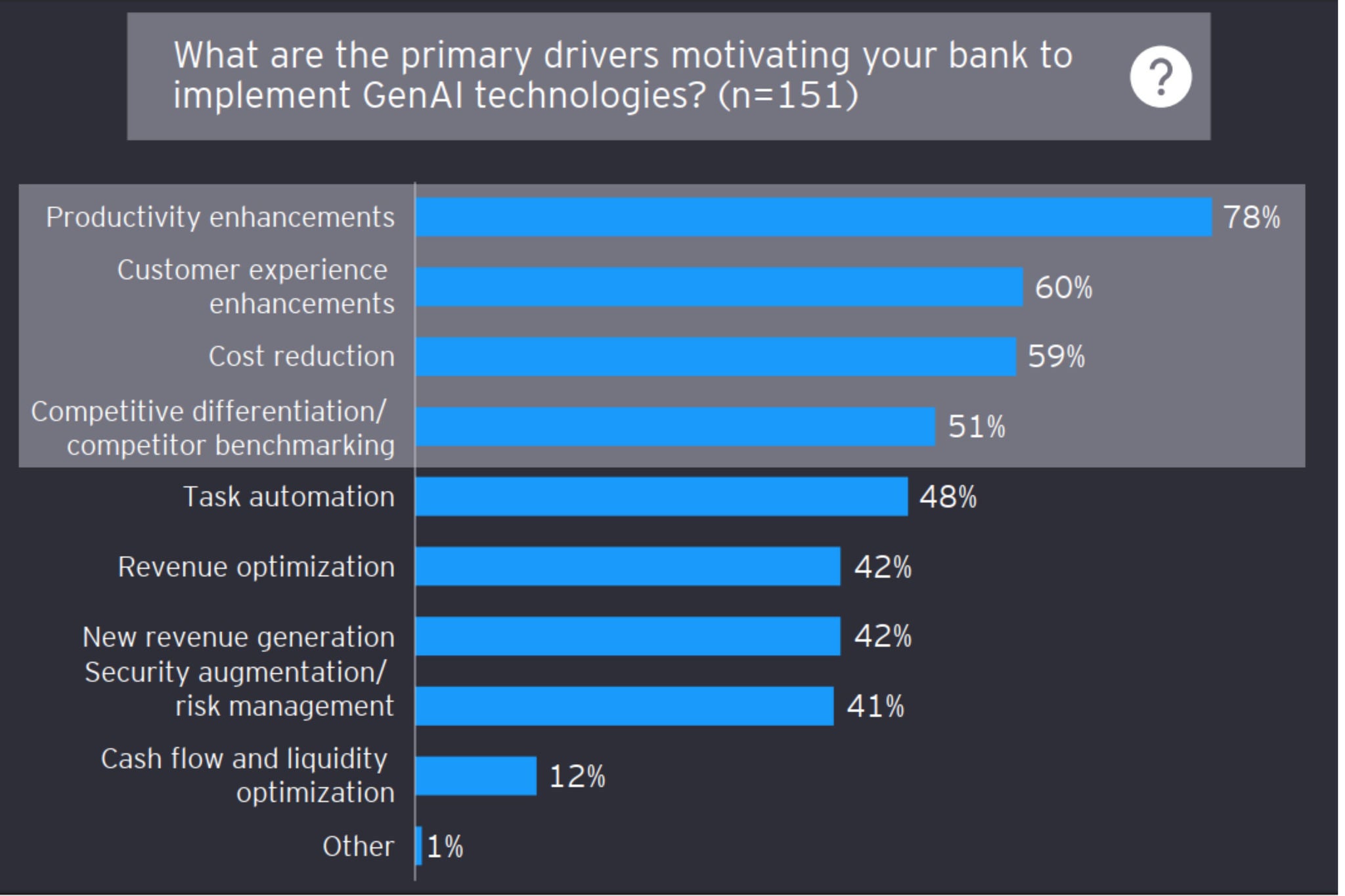
Advanced technology such as Gen AI, while in its early stages of adoption, will continue to be a growth accelerator as it optimizes processes and empowers the strategic delivery of customer focused solutions to drive new revenue growth.
Innovation will be the FS watchword this year
The evolving landscape of Southeast Asia’s financial services industry presents exciting opportunities for incumbents who are willing to embrace innovation.
Real-time payments, GenAI, embedded finance and legacy simplification are not merely trends but essential pillars for staying ahead in the market. By leveraging these technologies and concepts, financial institutions can enhance customer experiences, streamline operations and unlock new revenue streams.
As the industry continues to evolve, incumbents who remain proactive in harnessing innovation will not only stay competitive but also thrive in an increasingly dynamic and digital financial ecosystem.
Our related articles
How will embedded finance revolutionize industries in Southeast Asia?
How is embedded finance transforming the Asia-Pacific financial landscape, including its rise and opportunities within Southeast Asia’s digital economy?
How FIs will create value from the Singapore-Asia Taxonomy
Economic activities will be classified through a climate science-focused lens to support Singapore’s sustainable finance ecosystem. Learn more.
How APAC financial services leaders can accelerate tech transformation
APAC financial services are facing new challenges and opportunities for tech transformation. Discover what’s working and what’s holding organizations back.
Summary
In 2024, Southeast Asia’s financial institutions will have important opportunities to embrace innovation and ecosystem collaboration to find new growth areas. Competitive pressure from disruptors will push firms to invest in new and emerging technologies and trends, including Gen AI and embedded finance. Fortune will favor the bold.





