
COVID-19: Impact on Malaysian businesses
The severity of the COVID-19 impact on business is unprecedented. Weak economic and financial results, demand cut-backs, supply chain disruptions and knock-on effects of troubled sectors on employment are challenging most economies, including Malaysia’s.
Against this backdrop, EY initiated the COVID-19: Business impact survey to understand:
- The impact of COVID-19 and the Movement Control Order (MCO) on Malaysian businesses; and
- The measures and assistance that businesses need
The start of the journey towards economic recovery is contingent on rebuilding trust and confidence in the public and business realms and the deliberate intervention of the Government. Businesses need to work hand-in-hand with the Government to resume operations and kick-start economic activities. Meanwhile, the increasing need for higher technology capabilities to connect businesses, customers and supply networks is fast-tracking the world into digitalization. Malaysia must not be left behind.
Five highlights
- COVID-19 is a game changer for Digital Transformation
Most companies (83% LLs and 84% SMEs) highlighted difficulties in their online connectivity and communication with customers and suppliers, in addition to their need for better infrastructure. - Malaysian workforce adapted during the MCO despite facing connectivity, tools and HR policy challenges
Over two-thirds (69%) of companies experienced disruption in one form or another, with 53% of SMEs and 39% of LLs voicing the need for improvement. - Swifter re-opening of the economy is needed
Over half of the companies (60% of LLs and 56% of SMEs) cited the need for urgent relaxation of MCO restrictions. - Embracing the new normal requires incentives and appropriate policies
Close to 50% of LLs and 40% of SMEs suggested direct government aid and incentives (technology grants, tax relief and loan relief) are required. - Galvanizing Corporate Malaysia to work concertedly with Government is critical to rebuilding trust and confidence.
Survey background
The online survey received over 670 responses from large and listed companies and SMEs.
The achieved sample profile represents Malaysia’s economic structure.
In identifying the areas of support needed by businesses, the EY COVID-19: Business impact survey evaluated the key challenges across five areas:
COVID-19 managed to change the mindset of Corporate Malaysia towards Digital Transformation where previous efforts failed.
Survey highlights
The key survey findings from the five impacted business areas, segmented by large and listed companies and by small and medium-sized companies, are summarized as follows:
What do companies need?
1. Financial relief is paramount, as businesses both large and small take steps to maintain cashflow and operations.
2. Recurring “needs” themes among businesses include the following:
- Loan relief
- Tax reductions
- Grant assistance, particularly to manage costs for technology enhancements and upgrades
3. Additional measures include:
- Accepting digital documents for import clearances
- Clear guidelines on the opening and expansion of e-banking infrastructure
- Online training programs
4. Return to normalcy, including the removal of MCO restrictions, is key to achieving a quick recovery and restoring business confidence and growth.
Intervention areas
1. Relief from obligations
Financial relief is a top priority and includes loans, rent and taxes.
2. Technology solutions
Need for better connectivity, with tools to enable new ways of working
3. Business transformation
Assistance in adapting to new operations and processes
4. Certainty in the new normal
Clarity about the new normal and the ensuing expectations
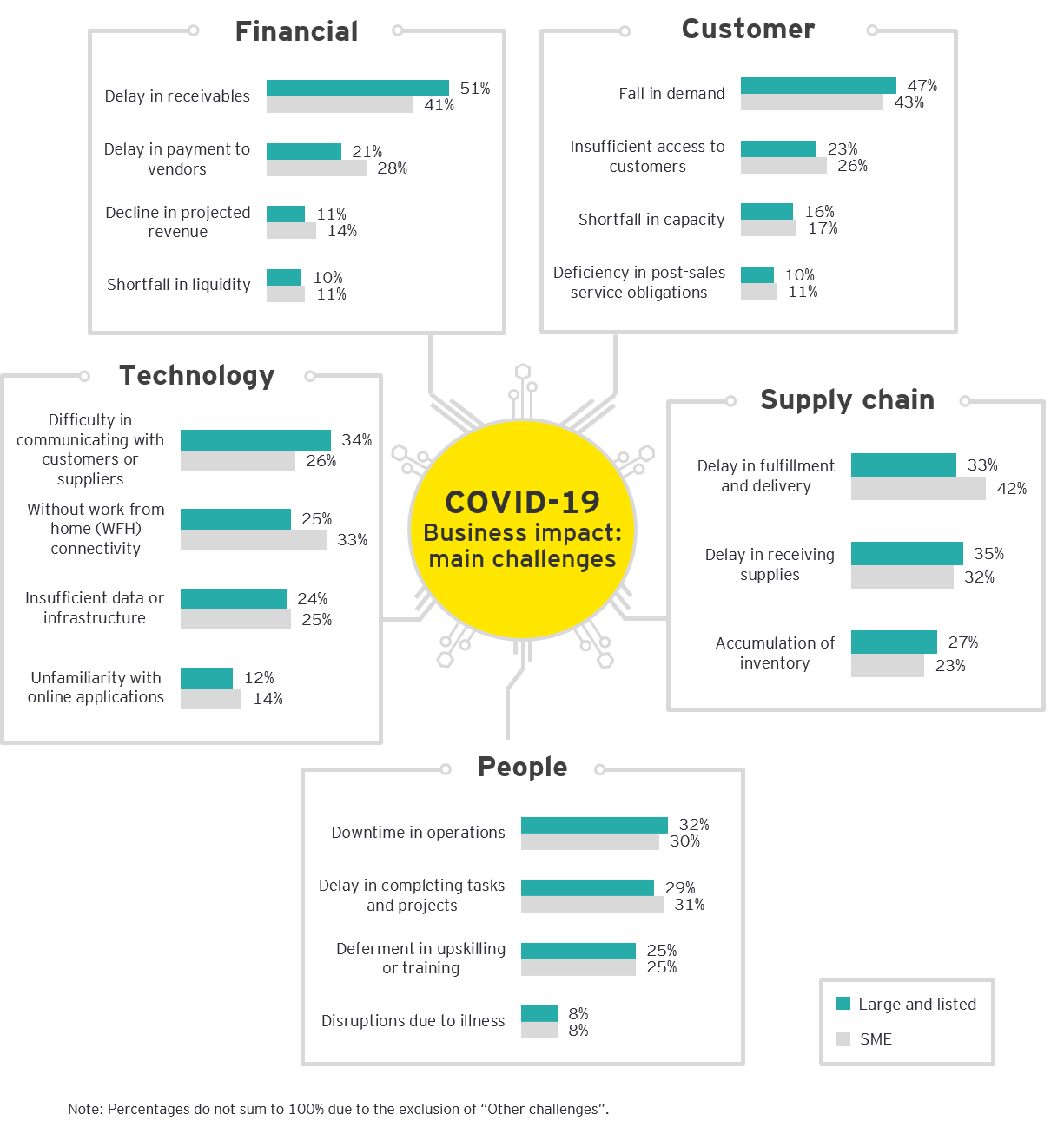
COVID-19 business impact: Financial
Top challenges: Financial issues include cashflow, liquidity, delays in receivables and declines in revenue.
Actions being taken: Nearly half of all companies surveyed indicated that cost-cutting measures are a priority. Others include cashflow management, re-prioritizing of business activities and investments and adjusting wages or applying for wage subsidies.
Intervention needed: Initiatives which reduce financial burdens or provide relief to loans and obligations are a priority.
COVID-19 business impact: Customer
Top challenges: Across large and SME companies, nearly half of the respondents have cited that a fall in demand is their key challenge.
Actions being taken: Half of the respondents noted that frequent communication with customers is key to planning and managing customer relationships.
Intervention needed: Over a quarter (26%) of large companies cited changes in Government policies as the most important assistance required, which include tax breaks, lower interest rates or fee waivers. For SMEs, relaxing MCO restrictions is key.
COVID-19 business impact: Technology
Top challenges: Nearly a third of large and listed companies cited communication with customers and suppliers as a major challenge, while SMEs highlighted WFH connectivity as a key issue.
Actions being taken: Companies are upgrading their technology and systems, and ensuring employees can connect.
Intervention needed: Improved connectivity is the priority need of businesses, followed by financial support in transitioning to technology-enabled processes and systems.
COVID-19 business impact: Supply chain
Top challenges: Large and listed companies cited delays in receiving supplies as the main supply chain challenge, while SMEs noted delays in fulfillment and delivery as their major challenge.
Actions being taken: Most large and listed companies are engaged in keeping suppliers informed through dialogue sessions on supply chain issues. For SMEs, payments and orders have been deferred whilst requesting for discounts from suppliers.
Intervention needed: Most companies are requesting for the waiver of cross-border and service taxes, along with additional credit facilities with banks.
COVID-19 business impact: People
Top challenges: 32% of all large and listed companies have faced downtime in their daily operations, while 31% of SMEs have experienced delays in completing tasks and projects.
Actions being taken: Close to a third of all companies are enhancing their remote working approaches with technical and connectivity support. Large and listed companies are also placing heavy emphasis on staying connected with employees.
Intervention needed: 38% of SMEs have prioritized applications for wage subsidies, while large and listed companies have placed equal importance on staff upskilling, wage subsidies and support with internet connectivity and working tools.
Stepping up


